Basic Data Structures and their frequently used methods in Java
Array:
- Creating : int [][] a1= new int [3][3];
- Size/length: a1.length
- Sorting
- Arrays to list:
String:
- toLowerCase()
- toUpperCase()
- replace(‘x’ , ‘y’) replaces all appearances of ‘x’ with ‘y’
- trim() removes the whitespaces at the beginning and at the end
- equals() returns ‘true’ if strings are equal
- equalsIgnoreCase() returns ‘true’ if strings are equal, irrespective of case of characters
- length()
- CharAt(n)
- compareTo() returns negative if string1 < string2 ;positive if string1 > string2; zero if string1 = str2
- concat() concatenates two strings
- substring(n) returns substring returning from character n
- substring(n,m) returns a substring between n and ma character.
- toString() creates the string representation of object
- indexOf(‘x’) returns the position of first occurrence of x in the string.
- indexOf(‘x’,n) returns the position of after nth position in string
- ValueOf (Variable) converts the parameter value to string representation
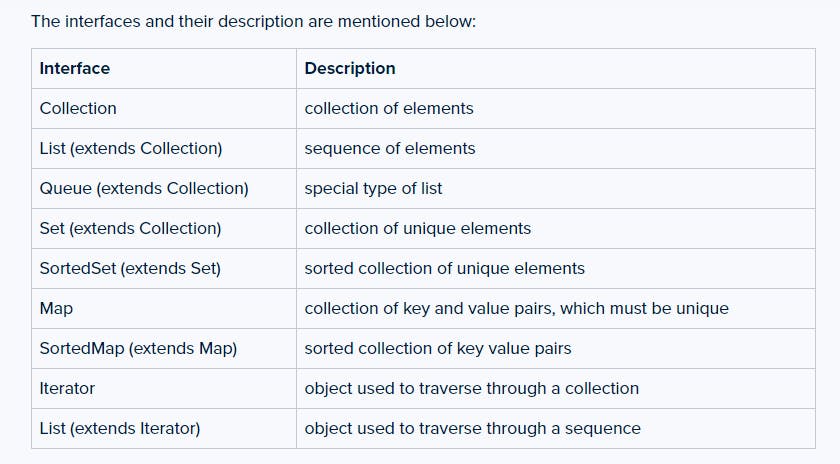
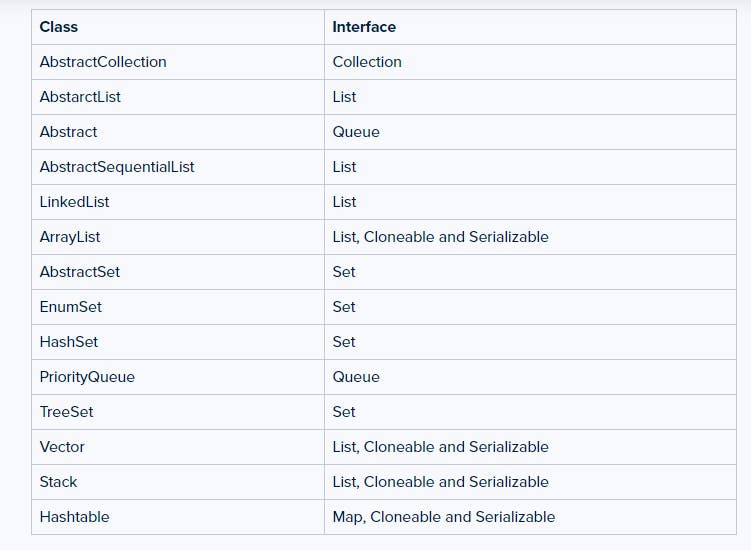
List:
- Creating list
Adding elements : a1.add(ele);
Removing elements: a1. remove(index)
a1.removeAll()- Accessing elements: a1.get(index)
- Size/length: a1.size()
- Sorting
- Removing duplictes
stackoverflow.com/questions/203984/how-do-i..
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(yourList); yourList.clear(); yourList.addAll(set); Of course, this destroys the ordering of the elements in the ArrayList.
useful links: stackoverflow.com/questions/24796273/incomp..
HashMap:
- Creating list
- Acessing elements
map.put(key,value); value = map.get(key) ; if( HashMap. containsKey(key)){} - Removing elements
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm.entrySet()) { String key = (String)mapElement.getKey(); // Add some bonus marks // to all the students and print it int value = ((int)mapElement.getValue() + 10); System.out.println(key + " : " + value); }- Sorting -
Priority Queue:
- What is the below initialization ?
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((n1, n2) -> n1 - n2);Ans: The constructor accepts aComparator<? super E> comparator. Basically the statement(n1, n2) -> n1 - n2is just a shorthand for
Comparator<Integer> result = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer n1, Integer n2){
return n1.compareTo(n2);
}
};
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(result);
More info :stackoverflow.com/questions/58714930/priori..
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(); is equivalent to PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((n1, n2) -> n1 - n2);
(Yet to update)
HashSet:
- Creating list
- Acessing elements
- Removing elements
- Printing elements
- Sorting -
TreeSet:
- Creating list
- Acessing elements
- Removing elements
- Printing elements
- Sorting -